Contents |
Introduction
This promises to be an important strategic year for CIOs, as public cloud service infrastructure providers (IaaS) such as AWS (Amazon Web Services) attempt to move their base from lower value mainly test and development environments to high value complete business-critical and mission-critical application stacks. The key to success for AWS, Google and other public cloud providers is moving further up the stack and reducing the work necessary just to keep the application running for small and large enterprise and government customers. Early indications from Wikibon members are that 40%-50% lower costs (or the equivalent in increased flexibility and time-to-value) can be obtained by moving to a rental base for complete cloud application services.
To assist users in looking at overall strategies, Wikibon is focusing research on highly converged infrastructure, and in particular at the definition, different deployment methods and business case for its deployment. The overall Wikibon thesis is that aggressive use of highly converged infrastructure deployments can reduce application infrastructure costs by about 50%, and be competitive with private clouds.
The savings come from vendors applying economies-of-scale to the development and deployment of converged infrastructure solutions. The supply model can differ, from hardware vendors putting together solutions with integrated software services, to public cloud providers packaging hardware and software services, to ISVs tightly integrating their software with hardware and services. Some very large-scale organizations may be big enough to generate their own economies-of-scale for some parts of IT.
The strategic importance of deploying highly converged infrastructure is less about the operational savings, and more about improving the ability of IT to combine low cost internal and external data with algorithmic components into improved and radically new ways of doing business. Key to developing a viable long-term strategy to achieve these goals is determining the physical and logical deployment topology of private, highly converged infrastructure, public cloud services and external data cloud sources.
To achieve long term profitability and viability, IT vendors will need develop business models enabling continuous cost reduction of the highly converged infrastructure hardware, software and services. The ability and commitment to update business models should be a key vendor selection criterion.
The starting point for this Wikibon research is focused on improving the productivity of DBAs using Oracle best practice methodologies, including highly converged infrastructure. As Oracle is among the most functional and widely deployed of business critical applications, we have focused on Oracle DBAs. Wikibon found the productivity of Oracle DBAs can be doubled with Oracle best practice. The most effective redeployment of DBA resources is assisting application developers to improve database design and reduce time-to-value for new projects.
Introduction to Wikibon Research
As Wikibon has pointed out in previous research, the business value of converged infrastructure topologies (Wikibon 2013) increases significantly as more higher-end stack components are integrated into a single managed entity (SME). The definition of SME includes:-
- An integrated delivery of the solution as a single component;
- Regular singular, global pretested updates to the solution;
- A single business partner for sales, deployment, maintenance and upgrades;
- A single hand to shake and throat to choke.
The more of the stack included, the greater the potential savings, with the inclusion of the whole stack and application into a SME by far the most effective in reducing enterprise IT costs. The economic driver beneath this finding is economy-of-scale. Maintaining a number of SMEs is much lower cost than maintaining an individual data center; the greater the number of identical SMEs, the greater the cost reduction potential. Clearly, creating SMEs around popular applications or common stacks will be the low hanging fruit. The public cloud providers is leading the continuous cost reduction, and the IT industry has to duplicate the public cloud economics to be successful.
As part of this research, Wikibon has recently conducted a series of in-depth interviews with Wikibon members who were using public clouds, including small, medium and very large organizations in both the private enterprise and government sectors. The findings were that the potential savings of taking this approach for new projects was in the order of 40-50%. However, significant investment in management time and IT organization were sometimes required to adjust to new ways of providing IT. For instance, there was often strong resistance from lines of business which have compliance and data security concerns. In general, smaller organizations were able to utilize public clouds more quickly, whereas larger organizations had significant investments in facilities, equipment and IT management, with more friction to change.
In addition, Wikibon recently interviewed Wikibon members who have adopted Oracle highly converged infrastructure solutions. From these findings and other research, Wikibon has calculated that IT executives can expect savings of 40% to 50% in costs or equivalent value by adopting an aggressive on-premise IaaS with the minimum number of SKUs, even after taking into account the higher costs of highly converged solutions. In a detailed analysis of Oracle DBA productivity shown in Figure 1, Wikibon shows that by adopting best practices in Oracle environments, database administrative (DBA) productivity is improved by 50%. Future Wikibon research will address the overall IT improvement from deploying Oracle best practices.
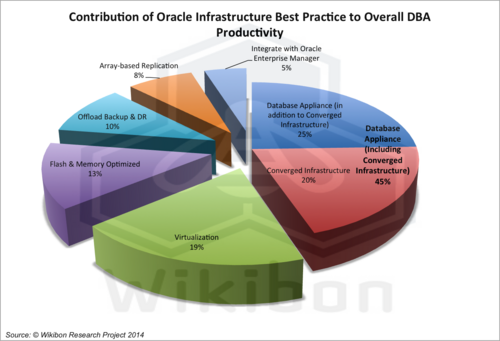
Source: Wikibon, 2014. See the analysis in the later section “Impact of Oracle Best Practice on DBA Productivity” for Assumptions & Calculations. This analysis was based on using a converged infrastructure reference model of a VCE Vblock system, which included virtualization, single SKU up to the middleware, flash and memory optimization, array based replication; a single hand to shake and a single throat to choke.
The fact that the savings from both the cloud and on-premise integrated models are similar is not surprising. Large ISVs will also be able to provide highly integrated, complete stacks with similar or even greater economies of scale. The potential cost reduction is not the only potential value. Having a stack that stable and common will make it much easier to deploy change and new systems, improving IT flexibility and time-to-value. Taking advantage of these fundamental IT improvements is a strategic necessity.
The key decision for CIOs and CEOs will be which strategic path to take, not just for one application but for the entire organizational portfolio of integrated applications and data. Increasingly, in-house IT resources will need to integrate into external application services and data, and the strategic path will need to include effective and efficient enabling of this imperative.
Wikibon Research Methodology
The IOUG report described day-to-day tasks of DBAs. In Figure 2 of this report the leading database administrative challenges were listed. Wikibon took this list as a starting point in discussions with database administrators, reworded activities and added some additional activities not included such as documentation, assisting application development (judged to be the most value activity) & “other”. The list in Table 1 below is ordered by time/effort required by our respondents:
These activities were used as a starting point for the discussion about the tasks themselves, the tools they used, and what tools/capabilities could make them even more productive. We focused in particular on the Oracle best practice elements shown in Table 2, shown in order of productivity value to DBAs.
The research looked at the impact of Oracle best practice elements individually and collectively on DBA productivity.
Impact of Oracle Best Practice on DBA Productivity
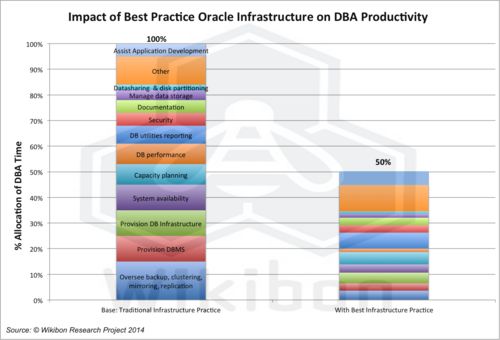
Figure 2 below shows the 100% allocation of DBA time in a traditional datacenter, as shown in Table 3 in the footnotes. The right hand side shows the allocation of time for a DBA with best practice infrastructure and support. Figure 2 shows that overall productivity is doubled (only 50% of the time is required to do the same work). Assisting application development (AD) is the activity that was assessed by DBAs as the most valuable. Only 5% of traditional DBA time could be applied to assisting AD; the best return on DBA resources would be applying all the DBA time to AD, which would reduce time-to-value and increase company productivity earlier. Optionally, CIOs can choose to reduce DBA costs.
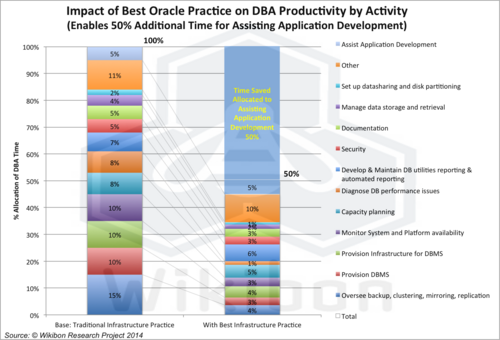
Source: Wikibon, 2014, left-hand column is pm-pa from Table 3 below, and the bottom half of the right-hand column is ym-ya from Table 3. The top half of the right-hand column represents the potential for increasing the assistance to the application development team (50%), which was judged to be the most valuable work component. This analysis was based on using a converged infrastructure reference model of a VCE Vblock system, which included virtualization, single SKU up to the middleware, flash and memory optimization, array based replication, a single hand to shake and a single throat to choke.
Figure 3 shows the resulting percentage contribution of Oracle best practice elements to DBA productivity. It shows that when converged infrastructure includes the database the combination provides the maximum contribution of 45% (25% for Oracle database convergence and 20% for other Infrastructure convergence) towards DBA productivity improvement. Virtualization (19%) and flash and memory optimization (13%) round out the top 4 elements that contribute 75% of the total DBA productivity improvement.
The detailed data sources and calculations for Figure 2 and Figure 3 are given in Table 3 and Note 1 in the Footnotes below
Conclusions & Recommendations
The thesis that a highly converged infrastructure deployment with a minimum of SMEs can reduce application infrastructure costs by about 40%-50% is supported by the initial Wikibon research on Oracle DBA productivity, and will be supported by future Wikibon research on overall productivity gains. The thesis that economies-of-scale from multiple deployment as the foundation of lower costs is again supported by the research, and by general experience curve theory. What is not known is the slope or shape (exponential, power of sigmoidal) of the experience curves, in particular the support cost components. The support cost components may be open to improved algorithmic approaches and the use of big data, which would lead to steeper and more sustained improvement. This understanding is important to assess - a steep and continuous experience curve for support costs would put an emphasis on volume as the key determinant of vendor success, whereas less aggressive experience characteristics might allow for a wider range of solutions focused on different industries or business processes.
Wikibon is certain of a significant reduction in IT costs as a result of converged infrastructure, and that all CIOs and senior business managers should be moving rapidly to adopt these technologies. There are three major alternatives for adoption:
- Adoption of converged infrastructure solutions (complete solutions or reference architectures) from hardware vendors or hardware vendor partnerships for different parts of the infrastructure stack;
- Use of public cloud services to provide some parts or a complete integrated application solution;
- Use of an application ISV fully integrated cloud solution.
The savings for all three alternatives come from vendors applying economies-of-scale to the development and deployment of converged infrastructure solutions. One important criterion for vendor choice will be an assessment of how well the vendor's business model drives continuous cost reduction of the converged infrastructure hardware, software and services. In general, organizations with a separate service organization with separate financial goals will find it harder to develop solutions that minimize the service requirements. Some very large-scale organizations may be big enough to generate their own economies of scale for some parts of IT. Wikibon believes it likely that all organizations will embrace a significant proportion of cloud services over time.
Wikibon believes that the delivery method for converged infrastructure is less important than enabling an organization to combine low cost internal and external data and algorithmic components into improved and radically new ways of doing business. Data is "heavy", and it takes significant time and resources to move it around a network. Although networks are increasing bandwidths, the volume of data is growing even faster. Designing a long-term data topology that allows flexible aggregation and exploitation of data resources, and allows all types of solutions to coexist is likely to be the best strategic approach. Migration of in-house workloads to mega-datacenters that have direct access to cloud services is likely to be an important part of that strategy.
Action Item: Highly-converged infrastructure offerings are maturing fast, and will almost certainly offer significantly lower costs than traditional in-house approaches. The more of the infrastructure, application, and support that can be included in the converged solution, the greater the savings will be. CIOs & CTOs should adopt integrated solutions in a way that allows the maximum flexibility in combining internal and external data and applications, and should design data and system topologies that minimize data movement.
Footnotes:
'Table 3:
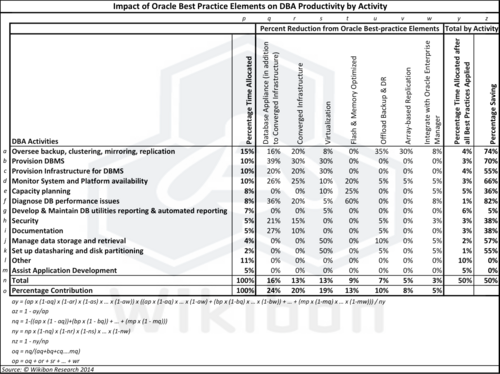
Source: Wikibon, 2014. The Wikibon estimates of productivity impact are shown in the table cells aq – mw, and the calculations for rows n and o, and columns u and z are shown the bottom half of the table.
Note 1: Calculations of DBA productivity in Figures 2 & 3
In Table 3 in the Footnotes, Wikibon assesses the improvement in productivity for each DBA activity by each Oracle best practice element. The left-hand column in Figure 2 comes from column p in Table 3, and is the percentage allocation in traditional Oracle infrastructure practice. The bottom part of the right-hand column in Figure 2 comes from column q, and shows the percentage of time after all the Oracle best practice elements (Table 2 above) are applied. The top part of the right-hand column represent the reallocation of the savings (50%) to the most valuable activity that a DBA does, assisting application developers in designing the database portion of applications. This raises the total amount of time allocated to AD support from 5% to 55%.
Row o in Table 3 shows the percentage contribution of each of the Oracle best practice elements to the overall productivity improvement of 50%, and is the input data for percentage pie-chart in Figure 3 above.